NOTICE: We've now moved all issue tracking to JIRA, to open an issue, look here.
Smarter Search for Bitbucket is a code, file and commit search service for Atlassian's Bitbucket. It's powered by Elasticsearch, which can be configured to be an external or internal Bitbucket service.
Table of Contents
- Installation Requirements
- Installing
- Features
- Administration
- Repository Settings
- Plugin Logging
- FAQ * Assuming I use the embedded Elasticsearch * a. What is the added load on my server? * b. Are there special HW requirements to support it? * If I use the global search, will it apply permissions restrictions (meaning if I have no access to a project/repository it will omit them from results)? * How do I control the Elasticsearch process? * How can I re-index all? * How can I know indexing status? * After a code change, how soon should I expect the search to find it? * How much disk space is used by this add-on? * Is there an API I can use for queries? * Please tell me, for every new commit, is the entire project indexed, or just the changes files in that commit? * Which version of Elasticsearch do I need for an external node?
- Reporting a Bug
- Contact Us
Smarter Search for Bitbucket requires that your server use git 1.8.5 or higher.
Smarter Search for Bitbucket is powered by Elasticsearch. Either an internal or external node can be used. This node handles all search requests and all repository indexing.
If you want to use an external node, you must use Elasticsearch 2.1.1. ####Internal Node By default, Smarter Search for Bitbucket spawns an internal elasticsearch node. The initial indexing of large repositories can potentially require a large portion of RAM. It is recommended to allocate Bitbucket 6GB of RAM for optimal performance. For instructions on changing the amount of memory available to Bitbucket, take a look at Altassian's documentation here.
As an example benchmark, Smarter Search for Bitbucket indexed the Linux code base which is approximately 15 million lines of code and half a million commits in 2-3 minutes with 6 GB of ram on non SSD harddives with an internal node. That said, it is recommended that for large codebases you use an external Elasticsearch node. For any concerns or questions, feel free to contact us.
####External Node For Bitbucket instances with large codebases and a lot of indexing, it's recommended to setup a separate Elasticsearch service. This will reduce the strain on Bitbucket for indexing, and should significantly improve performance. You can configure an external node in the settings page.
####Internal Node After installing the plugin in your bitbucket instance, you must enable indexing and trigger a reindex:
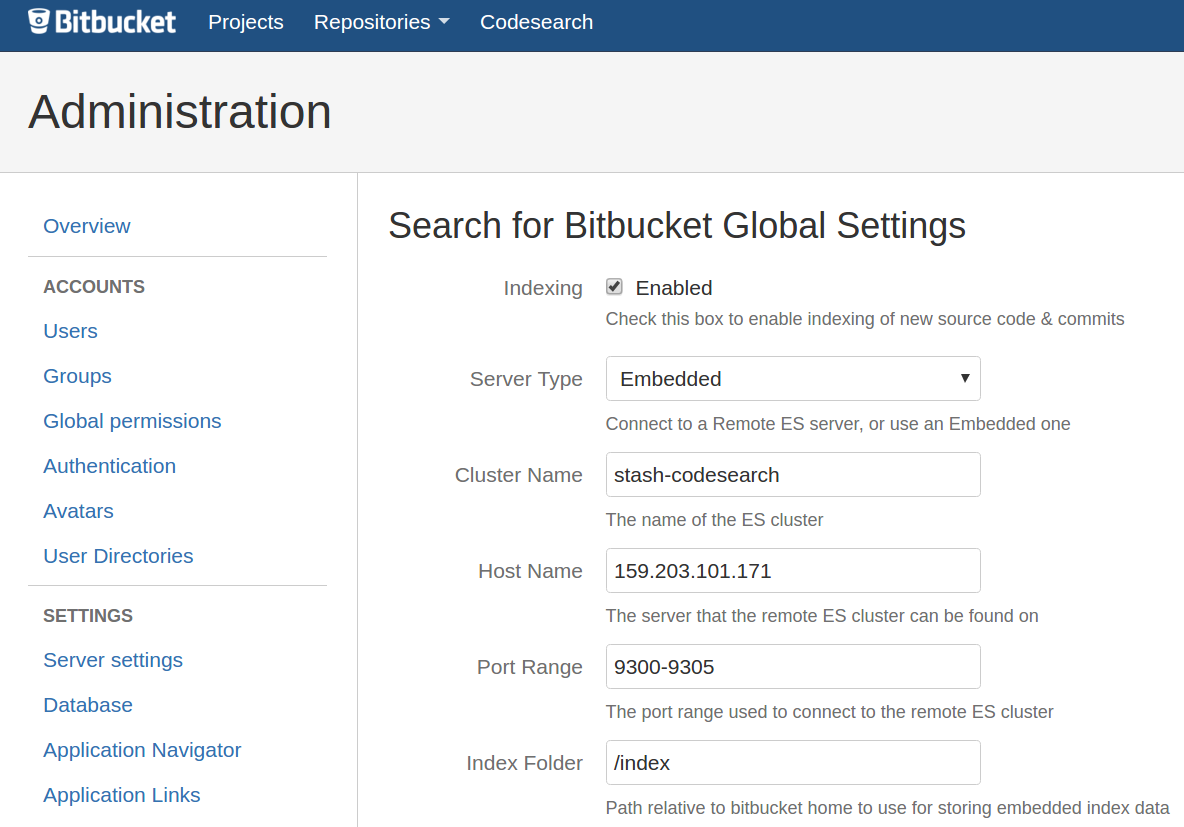
- Go to
Smarter Search for Bitbucket Global Settingspage in the Bitbucket admin panel. - Enable
Indexingby clicking the check box. - Click
Save and Reindexto save the settings and subsequently reindex all repositories.
####External Node You must first setup an external Elasticsearch cluster. For help on that, look here. Make sure you install the Delete By Query plugin as well. The scripts we've included will do this for you. Smarter Search for Bitbucket has a configuration page in the global settings to use to point to your Elasticsearch instance.
For testing purposes, we've provided some scripts for installing and running an elasticsearch instance. You can obtain an instance of Elasticsearch by running the provided bin/install-elasticsearch-instance.sh script. To run an Elasticsearch instance, run bin/invoke-es.sh. Make sure that elasticearch.yml is in the directory you are invoking Elasticsearch in so that the Elasticsearch configuration is picked up.
Once the node is setup, you must configure Smarter Search for Bitbucket:
- Go to
Smarter Search for Bitbucket Global Settingspage in the Bitbucket admin panel. - Enable
Indexingby clicking the check box. - Uncheck the
Internal ES Nodecheckbox. - Click
Save and Reindexto save the settings and subsequently reindex all repositories.
Smarter Search for Bitbucket will then start indexing all of your bitbucket repositories in the background. It will take a few seconds to a few minutes to finish depending on the number and size of your repositories. For large Bitbucket instances, it is recommend indexing to be done during non peak hours.
By default, only the master and develop branches are indexed. Individual repo admins may modify these settings. See below for instructions.
Since Smarter Search for Bitbucket is powered by Elasticsearch. It utilizes Elasticsearch's powerful Query String Syntax. This includes support for wildcards, regular expressions, fuzziness, and much more.
There are also many advanced filtering options. Here is a brief summary:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Search code, filenames and commits | Filter results to only code, commits, or filenames |
| Project keys | Filter results to specific projects |
| Repository slugs | Filter results to certain slugs. |
| Ref names | Filter results to certain refs |
| File extensions | Filter results to certain file extentions |
| Author/editor names or emails | Filter results to a specific author |
| Committed on or after/before (Commits only) | Filter results to a certain date range. |
Smarter Search for Bitbucket has advanced configuration settings. These settings should only be adjusted by advanced users.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Internal ES Node | Check this box to use an internal elasticsearch service. |
| Indexing | Check this box to enable indexing of new source code & commits |
| Indexing Concurrency Limit | Maximum number of concurrent indexing jobs |
| Max Filesize | Maximum size (in bytes) of source code files to index |
| Search Timeout | Timeout (in ms) of all search requests |
| Unhighlighted Extensions | Comma-separated list of file extensions to exclude from syntax highlighting |
| Preview Limit | Maximum number of lines to display for file previews |
| Match Limit | Maximum number of lines to display for file matches |
| Fragment Limit | Maximum number of match fragments to display for file matches |
| Page Size | Number of results to display per page |
| Commit Hash Boost | Boosting factor of results with matching commit hashes (relative to source code matches) |
| Commit Subject Boost | Boosting factor of results with matching commit subjects |
| Commit Body Boost | Boosting factor of results with matching commit message bodies |
| Filename Boost | Boosting factor of results with matching file names |
By default, only master and develop are indexed. Individual repo admins may modify these settings as follows:
- Go to the
Smarter Search for Bitbucket Repository Settingspage in your repository settings panel. - Change the ref regex to match your desired branches.
- Click
SaveorSave and Reindexto save the settings and subsequently reindex all repositories.
For example if we wanted to add the branch my-branch, we would modify the regex to look like :
HEAD|(refs/heads/(master|develop|my-branch))
You can also disable indexing for a specific repository.
The plugin has a robust logging system. The following log files exist for the plugin in the <bitbucket-home>/home/logs/ folder:
| Log file | Type of logs |
|---|---|
sfb-plugin.log |
All logs of nominal plugin operations, with any errors. |
sfb-plugin-debug.log |
All logs of nominal plugin operations, as well as debugging logs. |
sfb-elasticsearch.log |
Logs for only the internal Elasticsearch node. |
sfb-elasticsearch-debug.log |
Logs for only the internal Elasticsearch node, as well as debugging logs. |
| It is important to note that debug log information will not be recorded unless debug logging has been turned on in Bitbucket's settings. |
- Assuming I use the embedded Elasticsearch
- If I use the global search, will it apply permissions restrictions (meaning if I have no access to a project/repository it will omit them from results)?
- How do I control the Elasticsearch process?
- How can I re-index all?
- How can I know indexing status?
- After a code change, how soon should I expect the search to find it?
- How much disk space is used by this add-on?
- Is there an API I can use for queries?
- Please tell me, for every new commit, is the entire project indexed, or just the changes files in that commit?
- Which version of Elasticsearch do I need for an external node?
####Assuming I use the embedded Elasticsearch
#####a. What is the added load on my server? Initial indexing can potentially require large amounts of ram. We recommend allocating at least 6GB to the Bitbucket instance. As an example benchmark, our plugin indexed the Linux code base which is approximately 15 million lines of code and half a million commits in 2-3 minutes with 6GB of ram on non SSD harddrives with an internal node. Most of the strain on the system is generated by the initial indexing.
#####b. Are there special HW requirements to support it? No, but SSD's improve indexing speed tremendously.
If I use the global search, will it apply permissions restrictions (meaning if I have no access to a project/repository it will omit them from results)?
Repository permissions are applied to search results.
The internal node is embedded in the Bitbucket JVM. You can manually trigger indexing operations by going to global settings or the individual settings of the repository. If you want to see detailed logs on the Bitbucket side, just take a look at the logs. If you want even more detailed logs, you have to enable debug mode.
Go to the admin panel in Bitbucket, there should be a Search Global Settings option now under addons. Click Reindex all and it will trigger a reindex. Make sure indexing is enabled.
There currently isn't a last indexed status feature built in. This is something that's on our road-map.
All pushed changes generate events that our event handlers capture. It should be a matter of seconds until its indexed.
The indexer will pull Bitbucket repositories to the temp folder when it wants to index. So the repo will temporarily be stored on the server. The Elasticsearch node will worst case use around the same amount of space as Bitbucket is using to store repositories, so double your current disk-space to be safe.
You plugin currently does not have an API, but the Elasticsearch node does. You cannot currently query the internal node because of security reasons. You must use an external node if you want to query the node. Check here for more info on querying Elasticsearch.
Please tell me, for every new commit, is the entire project indexed, or just the changes files in that commit?
For every new commit, the plugin will do a diff of the changes and then apply those changes to the index. It doesn't reindex the whole repository because it doesn't have to.
You currently must use Elastichsearch version 1.5.2. We are planning on adding Elasticsearch 2.0 support in the near future.
If you encounter a bug, please open an issue here, and then send us the logs detailed in Plugin Logging to support.
If you want to get help, request a feature or report a bug, please email us at contact us or open an issue. We'd love to hear from you!