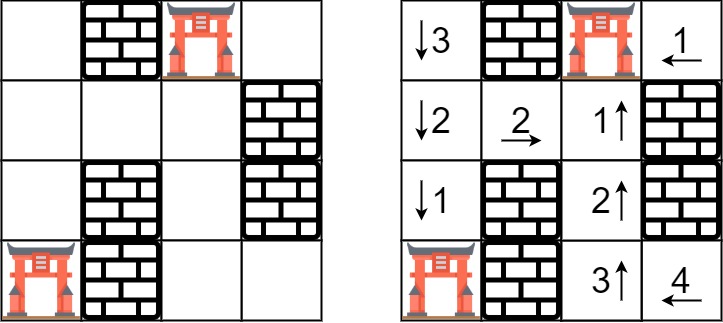
描述
你被给定一个 m × n 的二维网格 rooms ,网格中有以下三种可能的初始化值:
- -1 表示墙或是障碍物
- 0 表示一扇门
- INF 无限表示一个空的房间。然后,我们用 231 - 1 = 2147483647 代表 INF。你可以认为通往门的距离总是小于 2147483647 的。
你要给每个空房间位上填上该房间到 最近门的距离 ,如果无法到达门,则填 INF 即可。
实例
1、
输入:rooms = [[2147483647,-1,0,2147483647],[2147483647,2147483647,2147483647,-1],[2147483647,-1,2147483647,-1],[0,-1,2147483647,2147483647]]
输出:[[3,-1,0,1],[2,2,1,-1],[1,-1,2,-1],[0,-1,3,4]]
2、
输入:rooms = [[-1]]
输出:[[-1]]
3、
输入:rooms = [[2147483647]]
输出:[[2147483647]]
4、
输入:rooms = [[0]]
输出:[[0]]
提示:
- m == rooms.length
- n == rooms[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 250
- rooms[i][j] 是 -1、0 或 231 - 1
思路
1、先找到的所有门的位置
2、根据当前队列进行广度搜索
实现
/**
* @param {number[][]} rooms
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify rooms in-place instead.
*/
var wallsAndGates = function (rooms) {
const DOOR = 0;
const WALL = -1;
const INF = 2147483647;
const DIRECTION = [
[1, 0],
[-1, 0],
[0, 1],
[0, -1],
];
const roomsRow = rooms.length;
const roomsCol = rooms[0].length;
const doorQueue = [];
// 找到所有门
for (let i = 0; i < roomsRow; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < roomsCol; j++) {
if (rooms[i][j] === DOOR) {
doorQueue.push([i, j]);
}
}
}
while (doorQueue.length) {
const cur = doorQueue.shift();
for (const dir of DIRECTION) {
const newRow = cur[0] + dir[0];
const newCol = cur[1] + dir[1];
if (
newRow < 0 ||
newCol < 0 ||
newRow >= roomsRow ||
newCol >= roomsCol ||
rooms[newRow][newCol] !== INF
) {
// 不满足的条件
continue;
}
rooms[newRow][newCol] = rooms[cur[0]][cur[1]] + 1;
doorQueue.push([newRow, newCol]);
}
}
};实现-复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(mn)
空间复杂度:O(mn)
官方
private static final int EMPTY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static final int GATE = 0;
private static final List<int[]> DIRECTIONS = Arrays.asList(
new int[] { 1, 0},
new int[] {-1, 0},
new int[] { 0, 1},
new int[] { 0, -1}
);
public void wallsAndGates(int[][] rooms) {
int m = rooms.length;
if (m == 0) return;
int n = rooms[0].length;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int row = 0; row < m; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (rooms[row][col] == GATE) {
q.add(new int[] { row, col });
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] point = q.poll();
int row = point[0];
int col = point[1];
for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) {
int r = row + direction[0];
int c = col + direction[1];
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= m || c >= n || rooms[r][c] != EMPTY) {
continue;
}
rooms[r][c] = rooms[row][col] + 1;
q.add(new int[] { r, c });
}
}
}官方-复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(mn) 。如果你对直接得到时间复杂度有困难的话,我们可以从简单的情况开始。我们首先考虑只有一个门的情况,宽度优先搜索最多只需要 m * n 步就能到达所有的房间,所以时间复杂度是 O(mn) 。但是如果从 k 个门开始呢?一旦我们到达了一个房间,并记录下它的距离时,这意味着我们也标记了这个房间已经被访问过了,这意味着每个房间最多会被访问一次。因此,时间复杂度与门的数量无关,所以时间复杂度为 O(mn) 。
空间复杂度:O(mn) 。空间复杂度与队列的大小有关。我们最多将 m * n 个位置插入队列,所以空间最大为 m*n 。