-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 133
4. Upgrading or reinstalling macOS without wiping the system
Use the --reinstall parameter to initiate the reinstallation of the system volume without erasing it. This is commonly used for upgrading to a new version of macOS, but can also be used to reinstall the same version when troubleshooting, similar to reinstalling macOS via the Recovery Partition without first wiping the partition in Disk Utility.
If the --reinstall parameter is used alone, erase-install.sh will check for a cached installer in the working directory and in /Applications. If it finds one, it will use this installer for the reinstall process described below. If it does not find one, it will download the latest compatible installer for the system on which the script is running. This is also compatible with the --fetch-full-installer and --pkg parameters described elsewhere.
The reinstall process calls startosinstall (startosinstall is a command-line tool included in the macOS installer app).
The startosinstall command requires user credentials to be supplied when run on an Apple Silicon Mac. When running this script on an Apple Silicon Mac, the user will be prompted to enter a username and password via a dialog window. The current user is pre-filled in the dialog and chosen if skipped by the user, but a different user can be filled in instead. The script checks that the user exists, is a "Volume Owner", and that the password is correct.
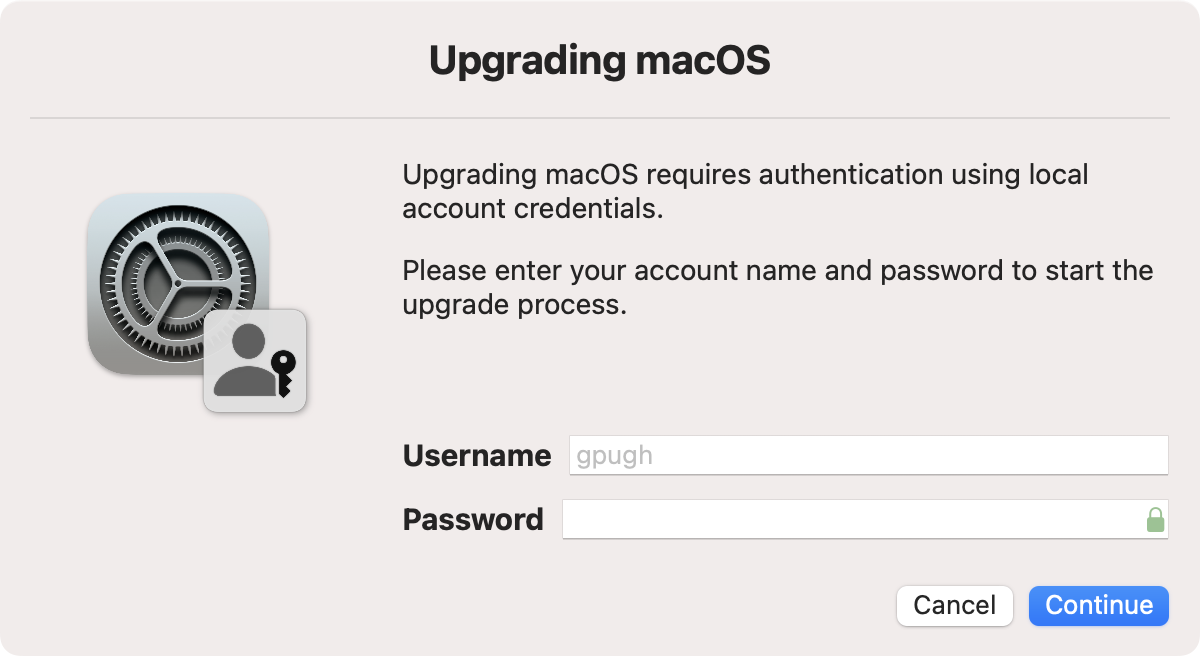
macOS Big Sur requires around 45 GB spare drive space to perform an upgrade using startosinstall. If this space is not available, the user is informed via a dialog and the script ends.
The specific amount of space required on the drive for reinstallation is not exact, and varies with each OS. You can override the default minimum space required for startosinstall to run with the --min-drive-space=NN or --min-drive-space NN parameter, where NN is a value in GB. Example --min-drive-space 30. It's up to you to test whether the figure you specify is enough.
A notification message is displayed during the download process. Once the download is complete, the window is closed and the script moves on to the reinstall process described below.
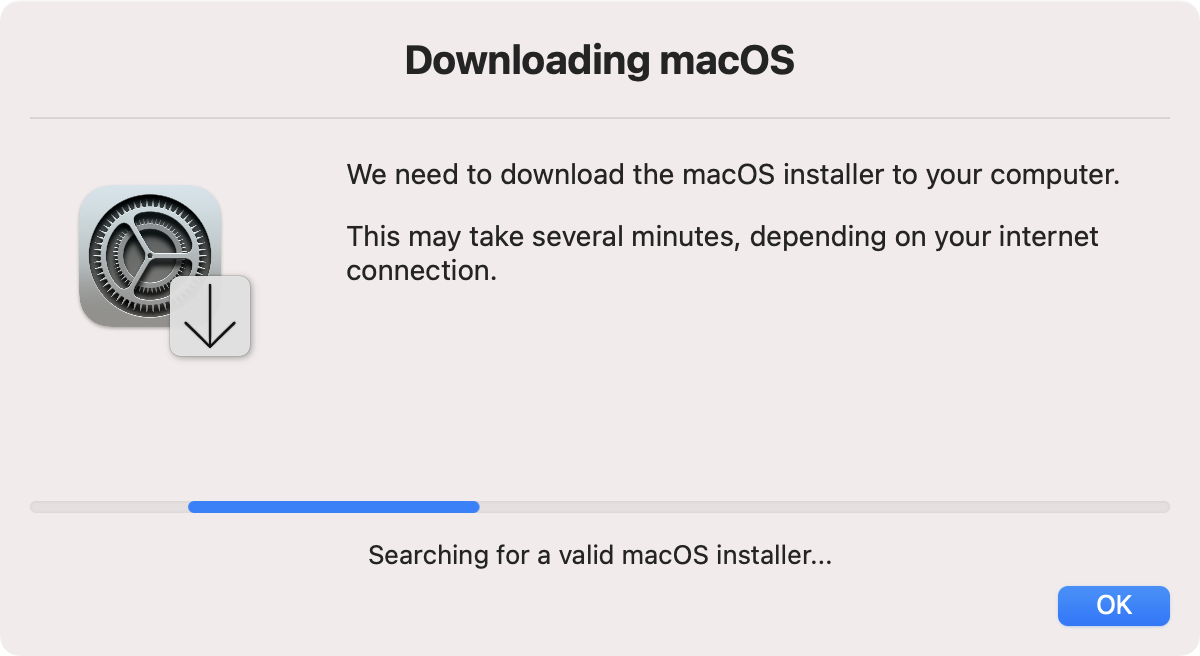
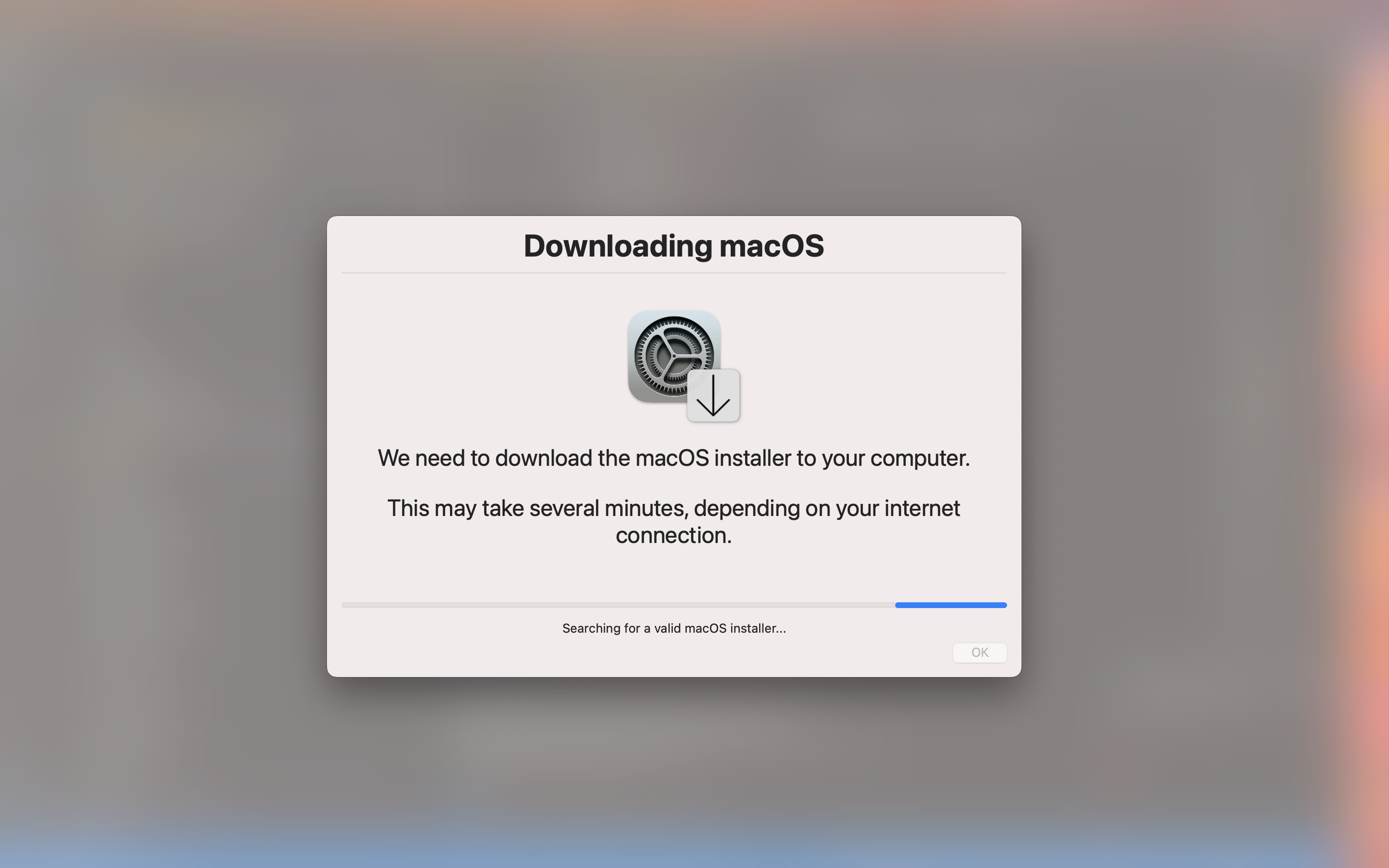
If the --fs parameter is added, the download dialog will be fullscreen.
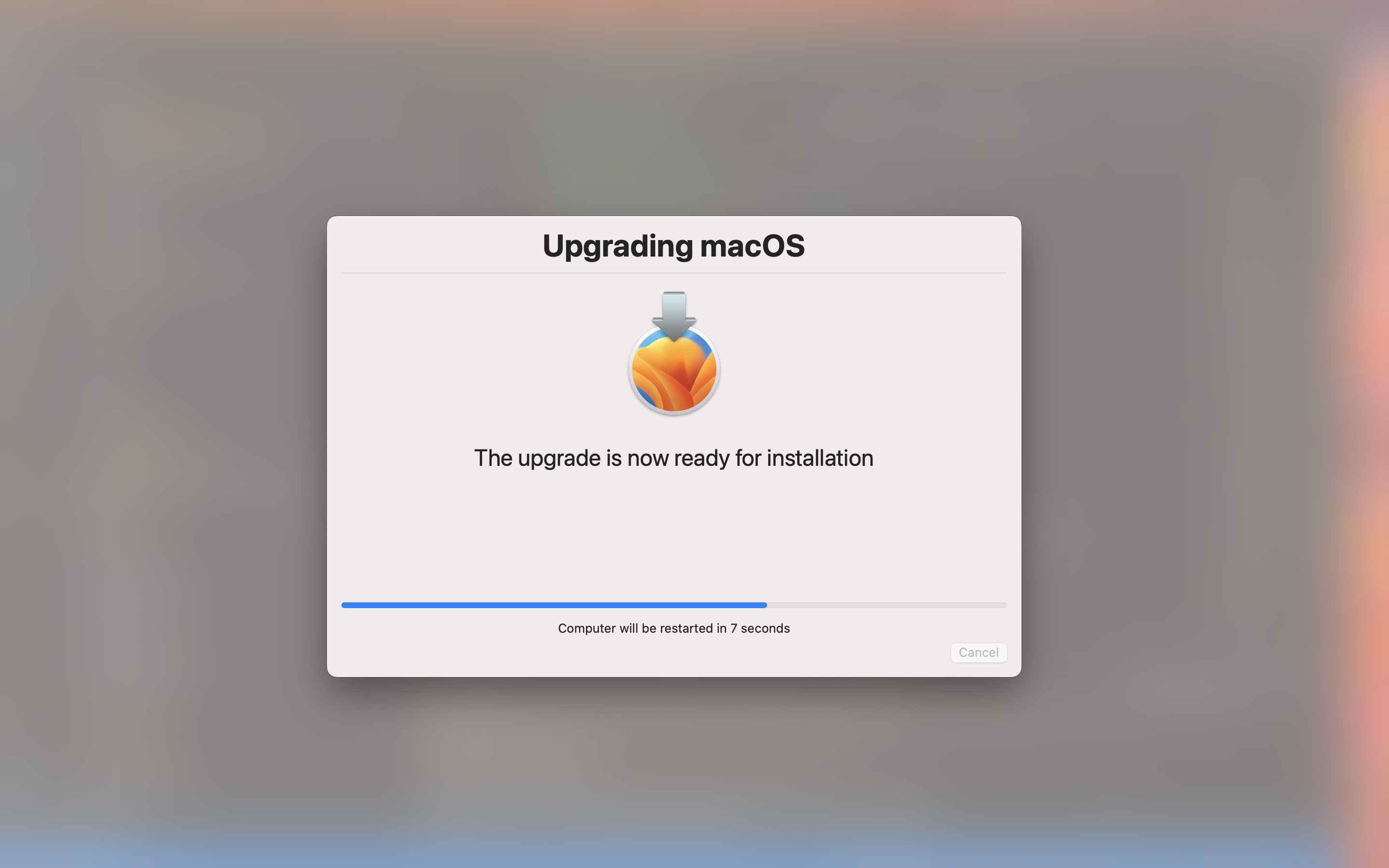
Once the reinstall process is ready to begin, another dialog is launched.
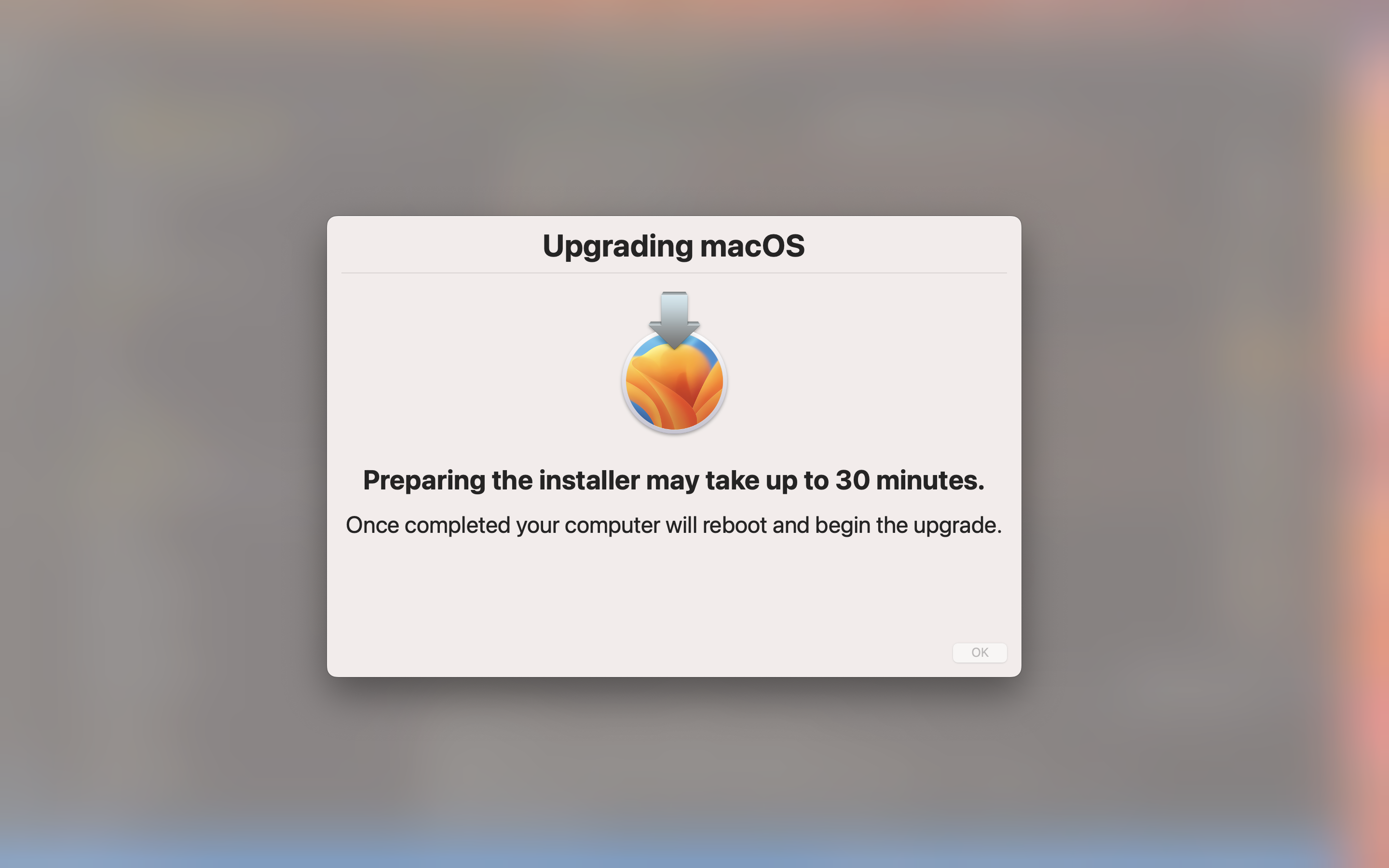
You can add the --no-fs parameter to switch to a utility window instead of the full screen window.

Shift+Cmd+C will quit the dialogs (not the script).
There are various additional parameters that can customise the reinstall workflow.
You can specify a specific OS, version or Build ID to download using the --os, --version or --build parameters. You can keep to the same OS as the current system using the --sameos parameter. You can keep to the same Build ID using the --samebuild parameter. See the section on downloading a specific version for more details of how these parameters work.
Recent versions of macOS have a long preparation phase followed by a short post-restart phase when reinstalling/upgrading. You can minimise the disruption to a user by allowing them to continue to work during the preparation phase. To do this, use the --rebootdelay option to allow a period of time after the preparation has completed for the user to save their work. If you specify a reboot delay of more than 10 seconds, the dialog window during the preparation phase is not full screen. A new dialog is shown when the preparation is complete.
If the --cleanup-after-use option is used, the script cleans up after itself after an upgrade/reinstallation is made. This is achieved by setting a LaunchDaemon that wipes erase-install's working directory upon startup.
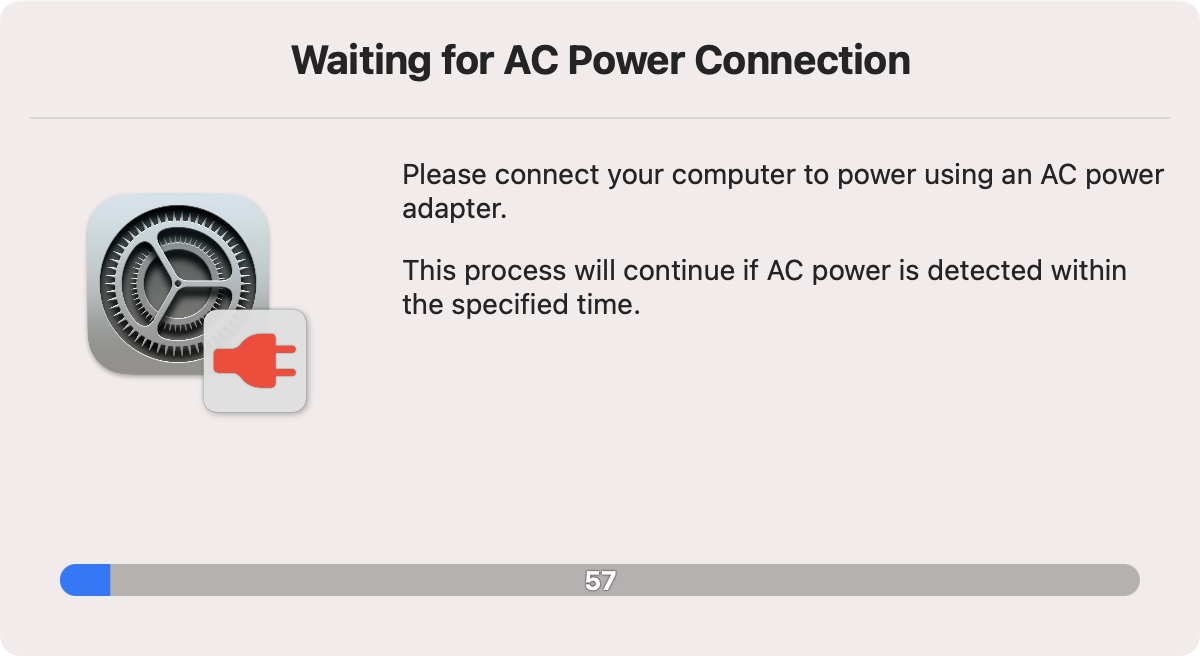
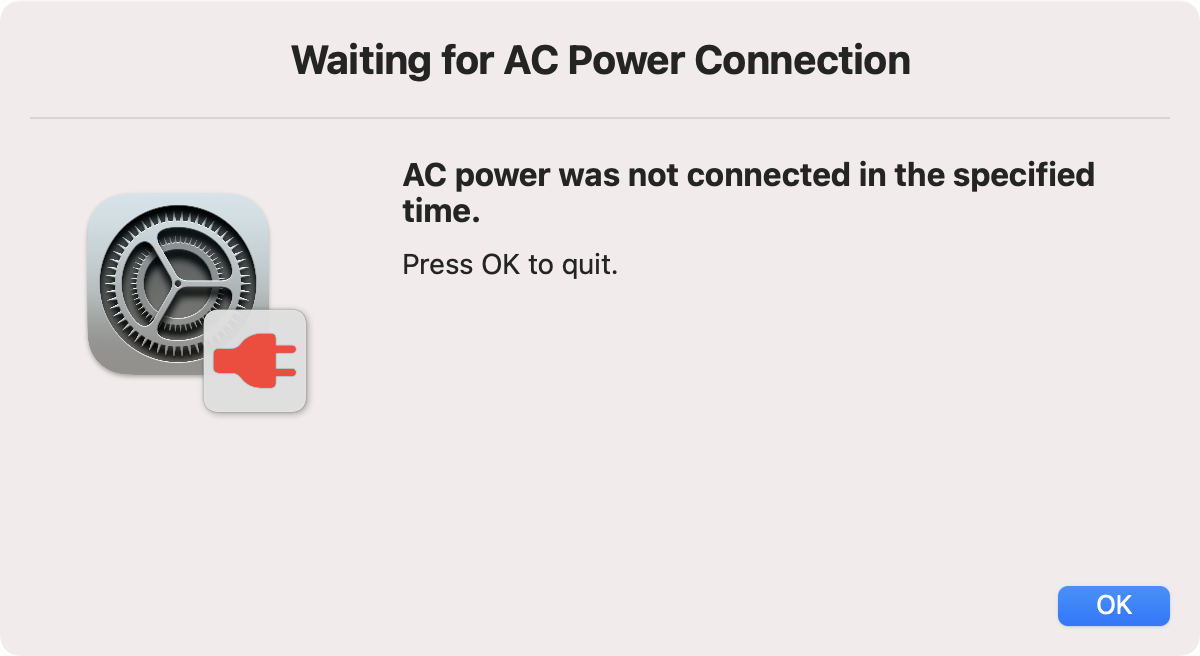
If the --check-power option is used, the script will check if the computer is connected to AC power. If it isn't, it will wait for a default of 60 seconds for power to be added, and otherwise fail.
The default time to wait can be altered by setting the --power-wait-limit option, e.g. --power-wait-limit 180 for 3 minutes.
This is the dialog shown:
Once the time is up, this is the dialog shown:
This parameter enables you to supply a shell command to run immediately prior to startosinstall running. An example might be:
--preinstall-command "jamf recon -department Spare"
Ensure that the command is in quotes.
This parameter enables you to supply a shell command to run immediately after startosinstall runs, but before the computer restarts. An example might be:
--postinstall-command "rm -rf /Applications/Google Chrome.app"
Ensure that the command is in quotes.
Note: this does NOT run after the computer restarts, but after startosinstall has finished preparing the update and immediately before the restart. So it is not useful for Jamf Pro users who wish to run recon. If you want to do that, create a separate policy that runs "Update Inventory" after every restart.
For testing out the script, you can add the --test-run parameter. This runs through the entire workflow up to but not including the startosinstall command. Instead, a sleep 120 command is run.